QuiryThink Learning Model for Academic Writing
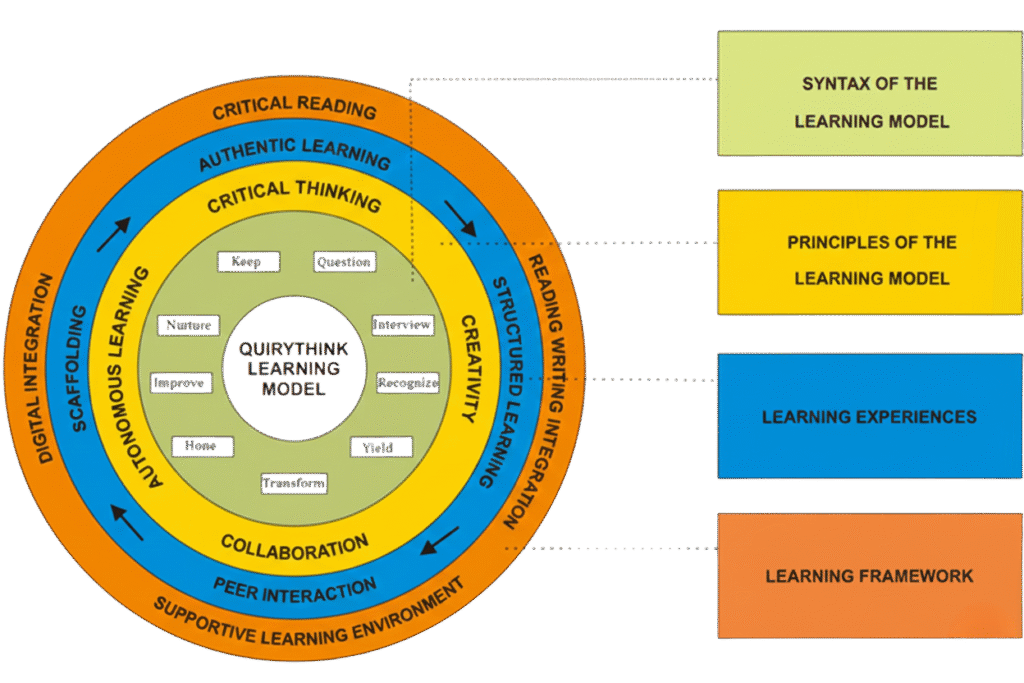
QuiryThink Learning Model Stages
- Question – In this stage, students are encouraged to raise critical questions about the characteristics of a well-written article that is suitable for publication in a reputable journal. These questions are not only intended to trigger their curiosity but also to guide them in identifying key elements of publishable academic writing. The formulated questions will then serve as the basis for the next stage, Interview.
- Interview – Students conduct interviews with lecturers, peers, or practitioners to seek answers and insights related to the questions they have previously formulated.
- Recognize – Students recognize patterns, essential findings, and the main issues that emerge from the collected information.
- Yield (Y) – Students begin outlining their writing based on the gathered insights. The lecturer provides digital tools and source materials to support the process, while students organize their ideas logically and start composing initial drafts. Peer sharing is facilitated by the lecturer to provide constructive input and further refine students’ initial drafts.
- Transform and Hone (T & H) – Students revise their drafts by incorporating feedback from lecturers and peers, enhancing the language, structure, and overall quality of arguments. This stage emphasizes improving the clarity and coherence of their manuscripts.
- Improve (I) – Students evaluate their writing using journal reviewers’ rubrics to test the quality and readiness of their work. The lecturer provides formative assessment with targeted comments, and students utilize Turnitin, Grammarly, or other AI tools to revise and refine their writing.
- Nurture (N) – Students perform their final revisions by carefully integrating all feedback and insights received during the Improve stage. This includes addressing remaining weaknesses in argumentation, clarity, and structure, ensuring the manuscript is polished and academically rigorous. The lecturer facilitates reflection and guidance during this stage, helping students consolidate their writing skills before submission.
- Keep (K) – At this stage, students ensure that their manuscripts are ready for journal submission. This involves completing a submission checklist, confirming compliance with journal guidelines, finalizing all references, formatting, and necessary documentation. The lecturer provides guidance on submission requirements and encourages students to double-check every aspect before officially submitting their work to a reputable journal.
Course Content
QUESTION STAGE
INTERVIEW STAGE
RECOGNIZE STAGE
YIELD, TRANSFORM and HONE STAGE
IMPROVE
NURTURE AND KEEP
